If you are a marijuana consumer, you would know that the aromas from different cannabis plants vary. You can also probably relate to taking a good sniff and inhaling these aromas when choosing a strain.
But have you considered what causes these aromas? They actually come from what is called Marijuana Terpenes, or Terpenoids. In general, Terpenes are the compounds found in cannabis that produce the unique smells.
There are a lot of different cannabis plants, and the aromas that vary from different strains serve as a guide to patients in developing a preference. Sweet, sour, citrus and strong are a few good examples of how these aromas are classified.
To understand how Terpenes impact your choice and what it may mean about the strain, we need to take a deeper look into Terpenes.
Where does the smell come from?

Terpenes and Terpenoids can be found as the primary component of essential oils in many types of plants and flowers. These essential oils are used as fragrances in perfume and are also used in medicine, including alternative medicine such as aromatherapy.
Terpenes serve as a major constituent in the Cannabis Sativa plant. There are 140 identified compounds within the cannabis plant which relate to terpenes.
They are not only responsible for the plant’s aroma or smell, but terpenes also go hand in hand and work together with cannabinoids in the cannabis plant to provide promising medical applications.
Examples of these are as follows:
- Acne therapy
- Treatment for anxiety disorder
- Antiseptic agents
What are Terpenes or Terpenoids in Marijuana?
Terpenes can be seen present in the glandular, hair-like follicles in the cannabis bud. Terpene production increases when a marijuana plant is exposed to more light, which is why you see them either grown out in large sunny areas or under strong artificial lights.
Terpenes are also present in the cannabis plant as it provides the plant with a natural barrier of protection against fungus, bacteria, insects and other environmental stresses that may affect the plant’s growth and development.
Essential oils in Terpenes are usually extracted from the cannabis plant material through the process of vaporization or by steam distillation.
THC vaporizes around the same time as Terpenes do, at around 157 degrees Celsius, although there are some Terpenes which are more volatile than others and may need an increase in heat to vaporize.
THC, the main psychotropic cannabinoid in the cannabis plant has already been studied a lot with regard to its medicinal value. However, the medicinal properties of many other Cannabinoids, Terpenoids and Flavonoids that have a huge impact in boosting the therapeutic effects have not and remains understudied.
Kinds of Terpenes in Marijuana

As already discussed, Terpenes are responsible for the varying aromas in cannabis and the physiological effects associated with it. Ultimately, the idea of knowing the aroma contributed by concentrations of specific Terpenes will help in identifying certain strains and their effects, allowing for more targeted production and use.
Companies have made ‘Terpene Wheels’ for marketing purposes, but this tool has also made it possible for patients to have a clearer choice when deciding which strain to use for their desired effects.
Below are some Terpenes and a quick run through of their properties:
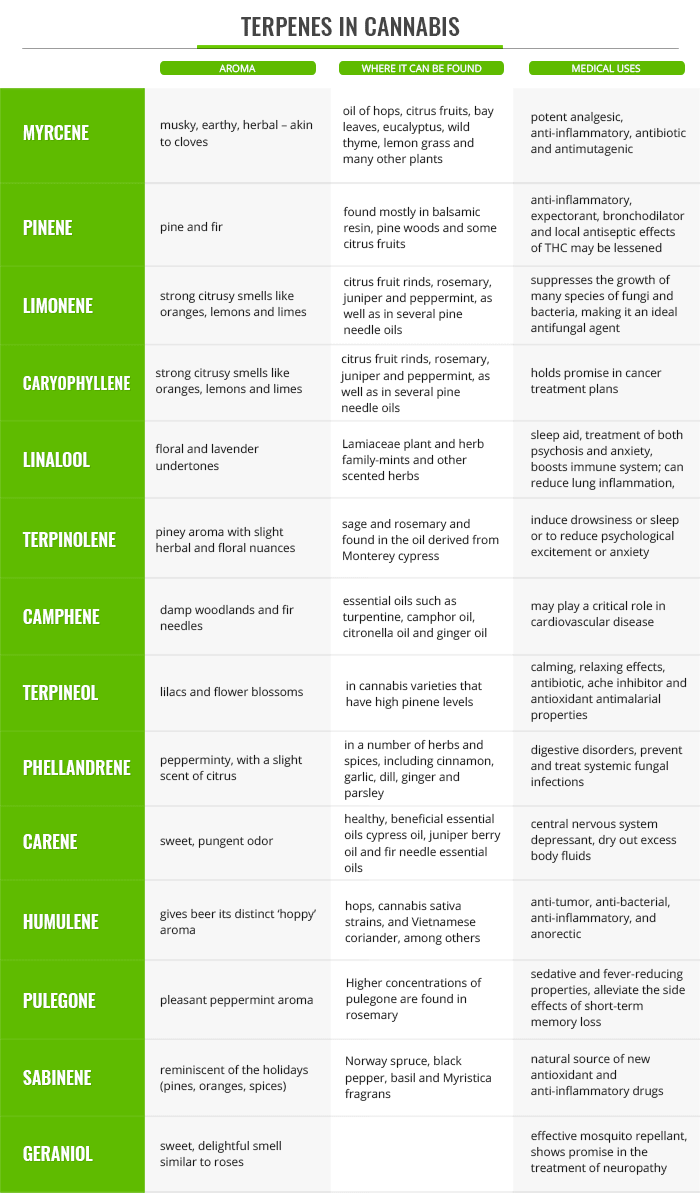
If you are interested to learn more about cannabis terpenes watch the below video with Dr Teh, Cannabinoid Clinician explaining them in great details:
Customizing Terpenes
It is now possible to predict and manipulate the effects of varieties by understanding and mapping terpene profiles. The breeder is given the opportunity to develop new and desired cannabis strains by basing their decisions on data. This, in turn, makes it easier for the patient to choose the ideal strain for the desired effect.
As more and more scientific developments are happening in the field of cannabis, the language of medical marijuana is becoming universal—easier to communicate and easier to understand.
What kind of aroma would you want to get from your weed?
Comment Your Thoughts Below!
- How to Use Waxmaid Honey Pen? - April 9, 2024
- How To Choose The Best Electric Dab Rig For Christmas - December 7, 2023
- Maintenance Matters: Keeping Your Glass Water Bong in Pristine Condition - October 9, 2023


